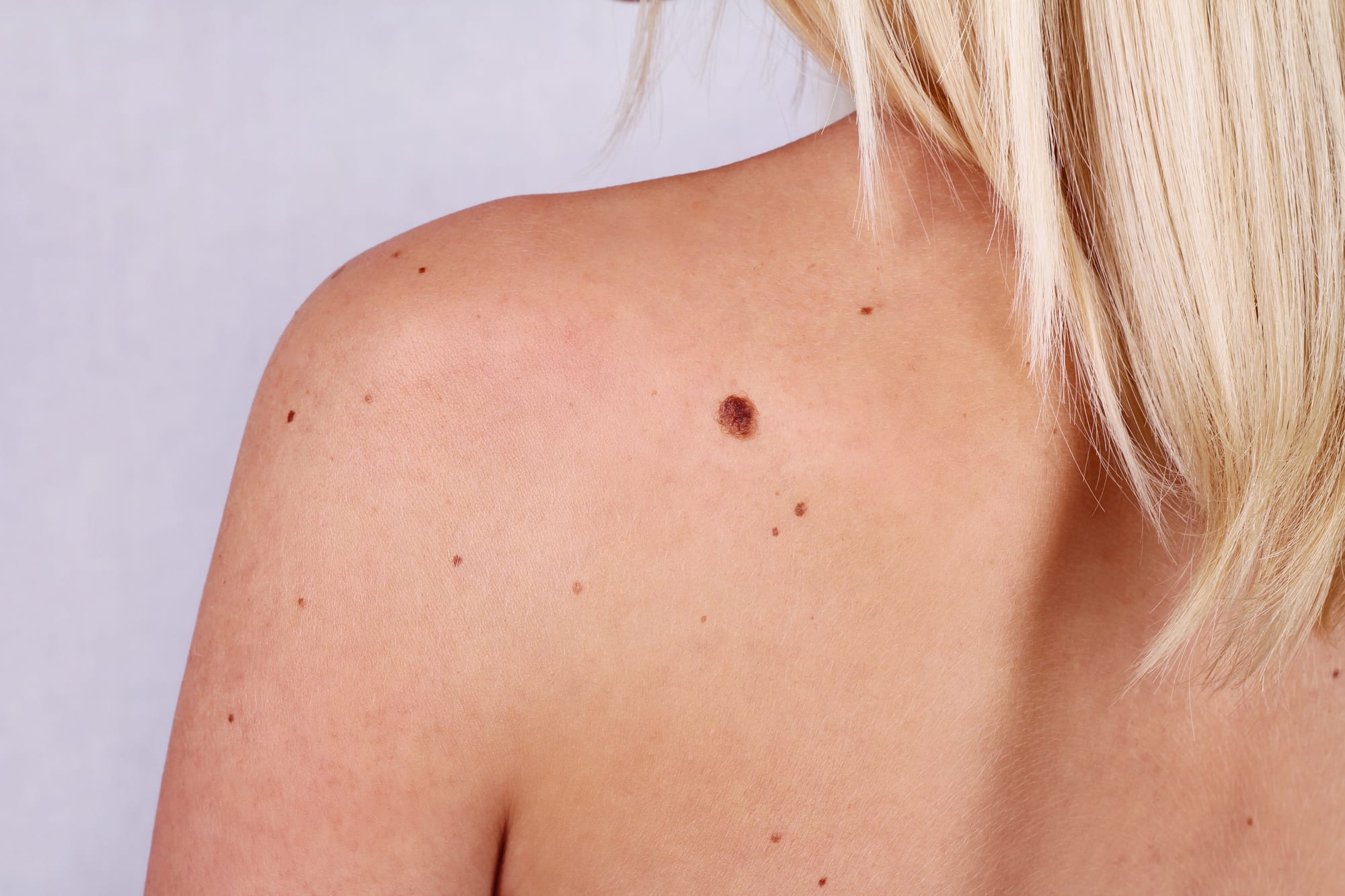
Skin moles are commonly found in people and come in various shapes, sizes, and colors. On average, a person can have anywhere between 10 to 40 moles on their body. Most moles are harmless, but it is recommended to get any atypically shaped or colored moles checked by a dermatologist. Thankfully with this additional information provided by Dallas Dermatology Partners, experts in the field of Dallas dermatology, you will understand these different types of moles and procedures to remove them.
Types of Mole
Melanocytes are skin cells that impart a natural color to the skin. Moles are formed when they grow in clusters on the skin instead of spreading throughout. Doctors are yet to determine what triggers this process, but it is believed that moles may be caused by hormones, genetics, prolonged sun exposure, and cancer in some rare cases.
Moles are categorized into three different types as follows:
Congenital Moles: These are the moles you are born with. They are usually raised, round, or oval-shaped in various sizes. These moles pose minimal risk of cancer, but bigger congenital moles may increase future skin cancer or melanoma risk.
Common Mole or Acquired Mole: These are harmless moles that start appearing on the skin after birth, usually by 20 or 30. These moles are also generally benign. However, it is suggested to visit a dermatologist if you have acquired moles ranging from 50 or more.
Atypical Mole or Dysplastic Nevus: These moles are irregular in shape and form, with odd coloring, and larger than a pencil eraser. People who have atypical moles have a higher risk of developing melanoma in the future.
Mole Removal Treatment
People sometimes find their moles unsightly and often get them removed through a medical procedure. Two procedures can be used for mole treatment based on location, color, depth, age, and skin type.
Shave or Punch Removal: Moles can be removed clinically with a blade without requiring any stitches or punches. This is a simple and in-office procedure that the dermatologist can perform after administering local anesthesia. However, knowing that this procedure may leave a linear scar that fades with time is important.
Surgical Removal: In certain cases, moles may have to be removed surgically if they are larger, deeply embedded in the skin, have a potential for cancer, or are not likely to respond to any other form of treatment. Such moles are removed through a surgical excision to remove the mole and prevent it from returning permanently. Surgical removal requires local anesthesia to numb the part and avoid discomfort. Once the mole is removed, the incision on the skin is closed with sutures. Like the punch removal procedure, surgical treatment may leave a linear scar behind that fades with time.
Consulting a Dermatologist
Most of the moles start developing from childhood into teenage years and young adulthood. These moles may change color, become raised, or sometimes fade away. It is recommended to consult a dermatologist if you notice that your existing mole is growing or if a new mole formation is observed on your body. Additionally, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist to discuss treatment options if you want to get your mole removed.